When you suffer from an illness anxiety disorder – also called hypochondria – you are scared of catching a serious illness or are convinced that you are currently suffering from or will suffer from a serious illness. If this fear is very strong and lasts longer than six months, we call it an illness anxiety disorder.
Symptoms
People with illness anxiety disorder are characterized by:
- compulsively checking their body for signs of illness
- avoiding or compulsively looking up information about diseases
- seeking reassurance from others
- continuous over-concern about having an illness
- physical reactions to the fear, such as a headache, palpitations or dizziness
- frequent visits to the doctor
Factors that sustain the anxiety
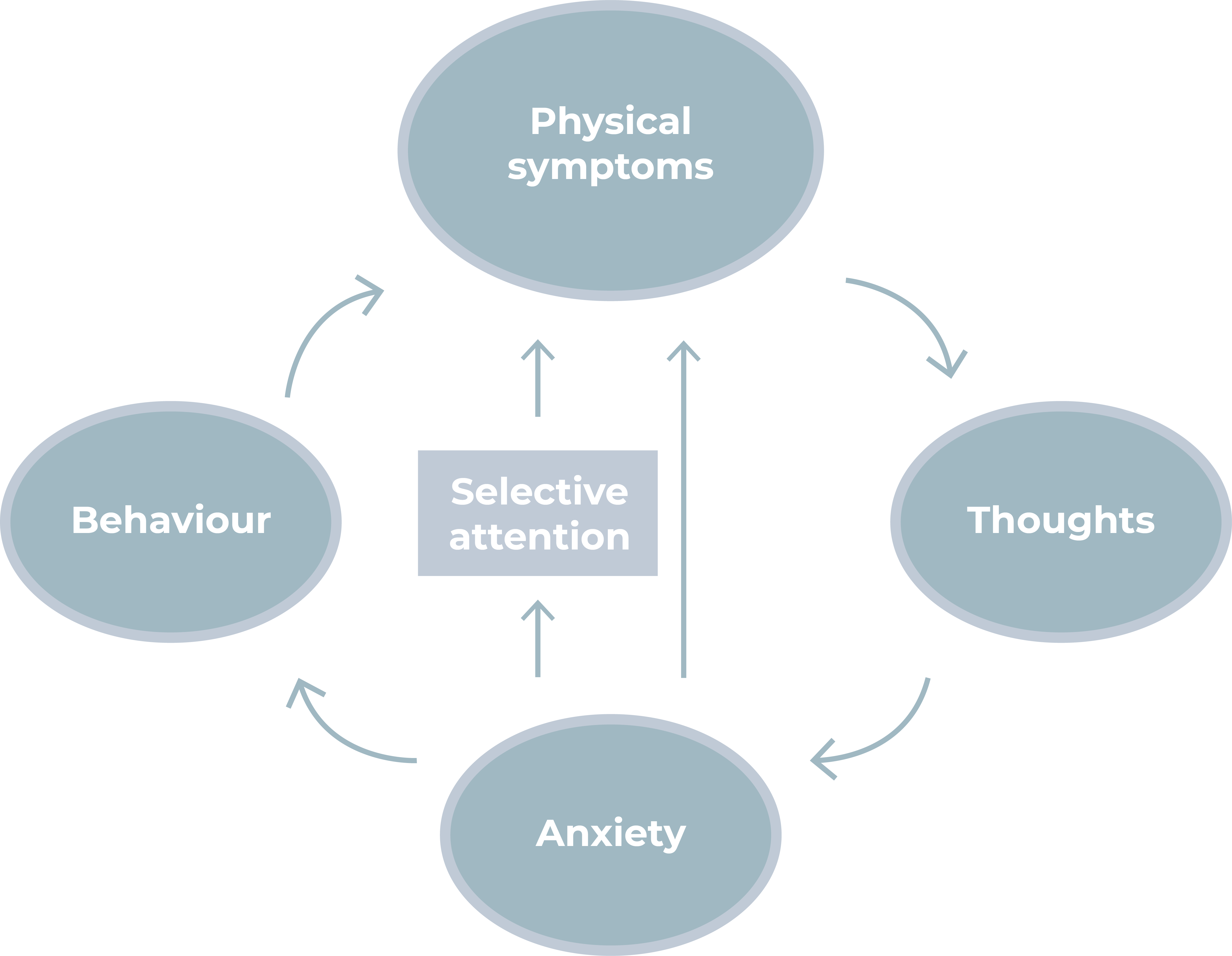
Often, there is a vicious circle of anxiety, existing of several factors that sustain the fear of an illness:
- Physical symptoms (with or without a medical explanation), for example chest pain that is interpreted from an anxious perspective.
- Negative thoughts can arise due to this interpretation, causing feelings (fear).
- This fear causes physical reactions (such as palpitations, stomach complaints, dizziness and muscle tension). Anxiety can also cause you to focus on these physical sensations even more.
- In response, you look for ways (behaviour) to reduce your anxiety, such as avoiding certain things or asking confirmation from loved ones or doctors.
Therapy
This vicious circle of anxiety sustains the symptoms. During the treatment, you will find ways to break this circle. Thoughts and behaviour are targeted as starting points for the treatment.
Treatment with Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) has been scientifically proven to be effective. The treatment aims to reduce the anxiety and over-anxiety caused by the physical sensations. The aim is not to reduce physical complaints or to exclude diseases, but to ease concerns about them. Instead, it examines the relationship between the thoughts that automatically arise and the emotions that you feel when you experience the fear of illness.
An important concept is the assumption that not only the physical phenomena cause the anxiety, but also the thoughts you have about them. In addition to your automatic thoughts, your behaviour will be observed.
With the help of cognitive therapy, we will try to detect, investigate and challenge these automatic thoughts. We challenge these thoughts with the help of a thought record. You will also be challenged to change your behaviour, for example, with the help of behavioural experiments.
Source:
Keijsers, G. P. J., Van Minnen, A., Verbraak, M., Hoogduin, C. A. L. & Emmelkamp, P., (2017). Protocollaire behandelingen voor volwassenen met psychische klachten.

 Print
Print